Botulinum toxin is one of the most commonly used medical and aesthetic treatments in the world. Despite its popularity, many people still feel nervous when they hear that it comes from a powerful toxin. This naturally leads to the question, how dangerous is botulinum toxin?
The word “toxin” can sound alarming, but in medicine, it is the dose, handling and professional control that determine safety. This guide explains how botulinum toxin works, why it is considered safe in clinical use, and when it can become harmful.
→ What Exactly Is Botulinum Toxin?
Botulinum toxin is a purified protein derived from a bacterium. In its raw form, it can be harmful. However, in medical treatments, it is carefully processed, diluted, and used in extremely small therapeutic doses. These doses are specifically calculated to provide medical benefit without causing harm.
In the UK, botulinum toxin is a licensed prescription medicine and is regulated for use by trained medical professionals.
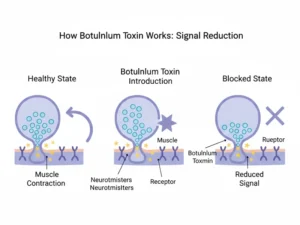
→ How Does Botulinum Toxin Work?
Botulinum toxin works by temporarily blocking nerve signals to specific muscles. When these nerve signals are reduced, the muscle relaxes. This effect is what makes the treatment useful for medical conditions such as muscle spasms, migraines, excessive sweating, and facial tension lines.
The toxin remains localised in the treated area and does not circulate freely through the body in harmful amounts.
→ How Dangerous Is Botulinum Toxin in Medical Use?
When used correctly by trained professionals, botulinum toxin has an excellent safety record. Millions of treatments are performed globally every year with very low complication rates.
The real risk does not come from the medication itself but from incorrect storage, improper dilution, poor injection technique, or treatment by unqualified individuals. In regulated clinics, strict safety protocols are followed to prevent these risks.
→ What Happens If It Is Used Incorrectly?
If botulinum toxin is injected incorrectly or in excessive amounts, it can cause unwanted muscle weakness, drooping of facial features, asymmetry, or difficulty with certain movements. These effects are usually temporary but can be distressing.
In rare cases, misuse can lead to more serious complications. This is why professional training and medical oversight are essential.
→ Common Side Effects
Most side effects are mild and temporary. Patients may notice redness, swelling or bruising at the injection site. Some experience a mild headache or temporary heaviness in the treated area. These effects usually settle within a few days.
Severe reactions are very rare in medical settings.
→ Who Should Avoid Botulinum Toxin?
Botulinum toxin may not be suitable for people with certain neurological conditions, those who are pregnant or breastfeeding, and those taking specific medications. A thorough medical consultation ensures that treatment is safe for each individual.
→ Can Botulinum Toxin Build Up in the Body?
Botulinum toxin does not accumulate permanently in the body. It is gradually broken down naturally over several months. This is why repeat treatments are safe when spaced appropriately and supervised by a clinician.
→ Why Choosing a Regulated Clinic Matters
UK clinics follow strict medical guidelines for storage, handling, and administration of botulinum toxin. Cold-chain storage, sterile preparation, and precise dosing protect both safety and treatment results.
Unregulated environments increase risk and should always be avoided.

→ Botulinum Toxin at Pinnacle Clinic Keighley
At Pinnacle Clinic Keighley, injectable treatments are carried out by trained professionals under strict medical protocols. Patient safety, transparency, and clear aftercare guidance are always prioritised.
→ Conclusion
So, how dangerous is botulinum toxin? In medical use, it is considered very safe when administered correctly by qualified professionals. The real danger lies in misuse, poor technique, and unregulated practice — not in properly delivered medical treatment.
Choosing a professional clinic ensures both safety and predictable results.


